The latest data from Universities UK International (UUKi) shows continued growth in the number of foreign students enrolled in transnational education programmes (TNE) offered by British institutions.
The scale of UK higher education transnational education 2019–20 reports that there were more than 4,53,000 students from 225 countries and territories pursuing qualifications from 156 UK institutions in 2019/20. This represents year-over-year growth of nearly 11% for the year leading up to the start of the pandemic, and overall growth of roughly 17% over the previous five years.
Just over half (50.3%) of those students were based in Asia, but significant proportions were also enrolled from the European Union (16.5%), the Middle East (13.1%), and Africa (10.7%). The following table highlights the top 20 countries by UK TNE enrolment.
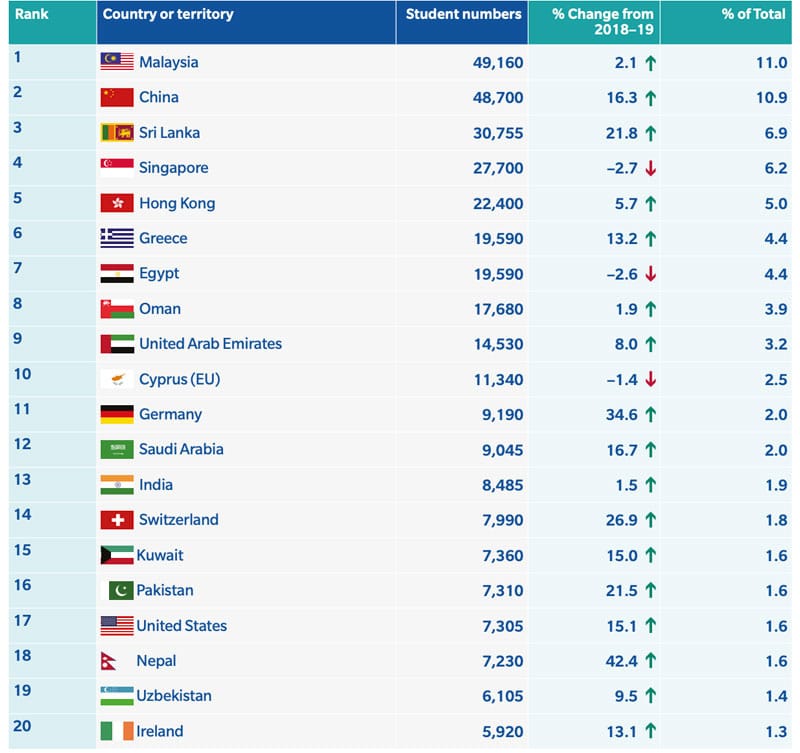
“Diversification of numbers to a more extensive number of countries will be crucial,” adds the report. “While numbers in China or Sri Lanka increased at double digit rates, there were few new territories in the ‘top 20’ host destinations. The [UK’s] International Education Strategy identifies priority countries such as India, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, Vietnam, and Nigeria, where student numbers are still relatively low. Regulatory reform in those markets coupled with UK government support should help ensure a more diversified picture emerges.” In addition, “Europe will continue to play a key role. Despite the UK leaving the EU (or partly because of it) the EU is still a crucial region both in terms of student numbers and the diversity of providers and types of provision. Given cultural and geographical proximity, and the protracted effects of Brexit in student recruitment, ensuring a regulatory environment as frictionless as possible framed in the UK-EU trade and cooperation agreement will be key to maintain growth.”
Delivery modes and level of study
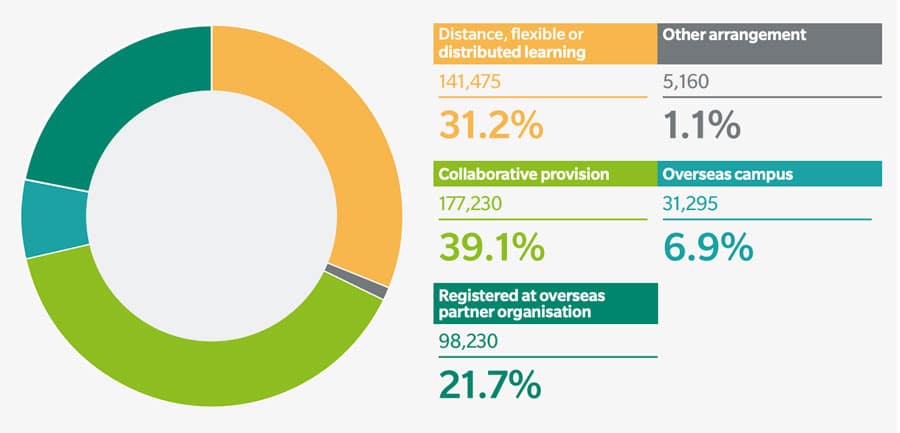
As in previous years, UUKi reporting on TNE maps the full range of delivery models for offshore programmes, including distance/distributed learning, branch campuses, and collaborative delivery with an overseas partner. The report notes, “In 2019/20, 39.1% of UK TNE students were studying through collaborative provision (up from 24.7% in 2018/19), 31.2% were studying through distance, flexible, or distributed learning (up from 18.1%), and 6.9% were studying at overseas campuses (up from 4.3%).”
This distribution (for 2019/20) is reflected in the chart below. For the most part, overall TNE enrolment growth between 2017/18 and 2019/20 has been driven by an expansion of collaborative provision arrangements and by greater participation in the distance, flexible, and distributed learning.
The report notes as well that most TNE students are pursuing a UK degree, with 65% of all 2019/20 enrolments in undergraduate degree programmes and just about 32% in postgraduate studies.
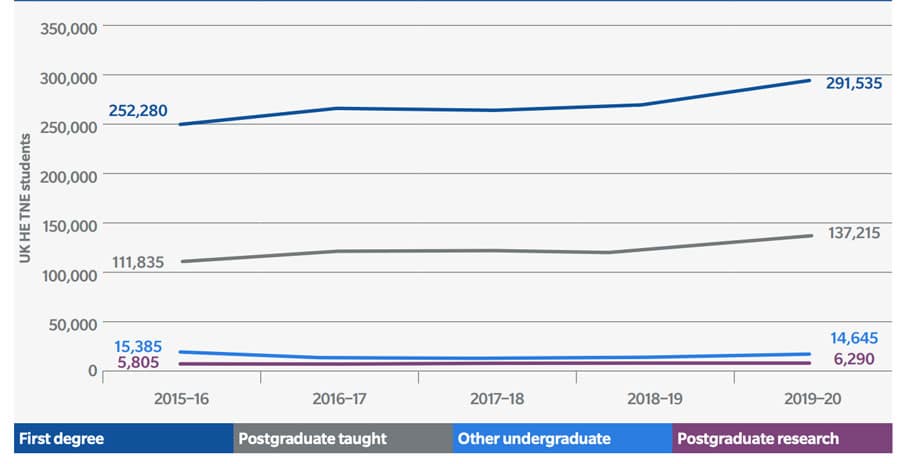
An obvious question that hangs over the 2019/20 numbers is how they may have changed during COVID. On this point, the report notes that, “Distance, flexible, or distributed learning is an increasingly important component of UK providers’ TNE portfolio,” and estimates that, “as a result of the pandemic, there could be in excess of 400,000 students studying at least partly online across borders in 2020/21 (although data on this cohort will not be available until 2022).”
Read all the Latest News here. Follow us on Facebook, Twitter, Instagram, and LinkedIn.

















Add comment